SEARCH
Japan launches world's first wooden satellite!

SHARE IT
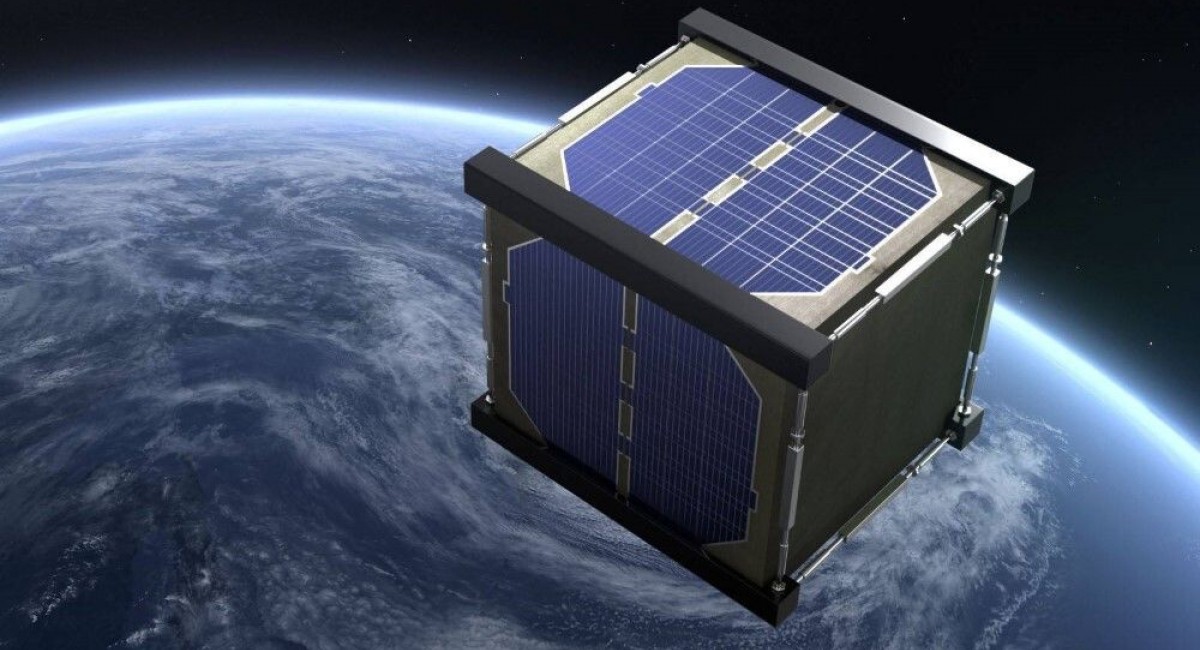
In an effort to test the material's longevity, Japanese researchers launched the world's first wooden satellite into space. Kyoto University academics collaborated with Sumitomo Forestry to create the wooden satellite known as "LingoSat," which comes from the Latin word for wood.
The wooden satellite was flown to the International Space Station (ISS) on a SpaceX mission before being deployed in orbit 400 kilometres above Earth to see how it performs in space. The LingoSat, a palm-sized satellite, was built of wooden wood.
Takao Doi, an astronaut who has flown on the Space Shuttle and studies human space activities at Kyoto University, stated that "with timber, a material we can produce ourselves, we will be able to build houses, live and work in space forever." He stated that because "Metal satellites might be banned in the future if we can prove our first wooden satellite works, we want to pitch it to Elon Musk's SpaceX."
The milestone is the first stage in a 50-year plan to plant trees, build timber houses, and create areas on the Moon and Mars. When discussing the possibility of a wooden satellite, Kyoto University forest science professor Koji Murata stated, "Early 1900s aeroplanes were made of wood. Wooden satellites should be feasible, too".
The two primary motivations for sending a wooden satellite into space are to test the endurance of wood when exposed to the harsh conditions of space. If the results are positive, researchers will be given the go-ahead to develop wooden structures for space missions.
Second, a wooden satellite has a low environmental impact as it approaches the end of its life. Decommissioned satellites must re-enter the atmosphere to prevent becoming space trash. Metal satellites emit aluminium oxide when they re-enter the atmosphere, whereas wooden satellites just burn up and disappear. Given the vast number of satellites circling the Earth, wooden satellites have the potential to dramatically reduce space debris.
MORE NEWS FOR YOU

 Help & Support
Help & Support