SEARCH
OpenAI unveils a dedicated translation tool to challenge Google
SHARE IT
For years, the digital translation landscape has been dominated by a single, colossal entity. Google Translate has served as the default utility for students, travelers, and professionals alike, offering a quick, albeit sometimes imperfect, bridge between languages. However, a quiet revolution is brewing within the laboratories of OpenAI, the company that ignited the current generative AI boom. Without fanfare or a grand press event, OpenAI has begun testing a dedicated interface that takes direct aim at Google’s hegemony, offering a glimpse into a future where translation is not just about swapping words, but understanding intent, tone, and context with unprecedented depth.
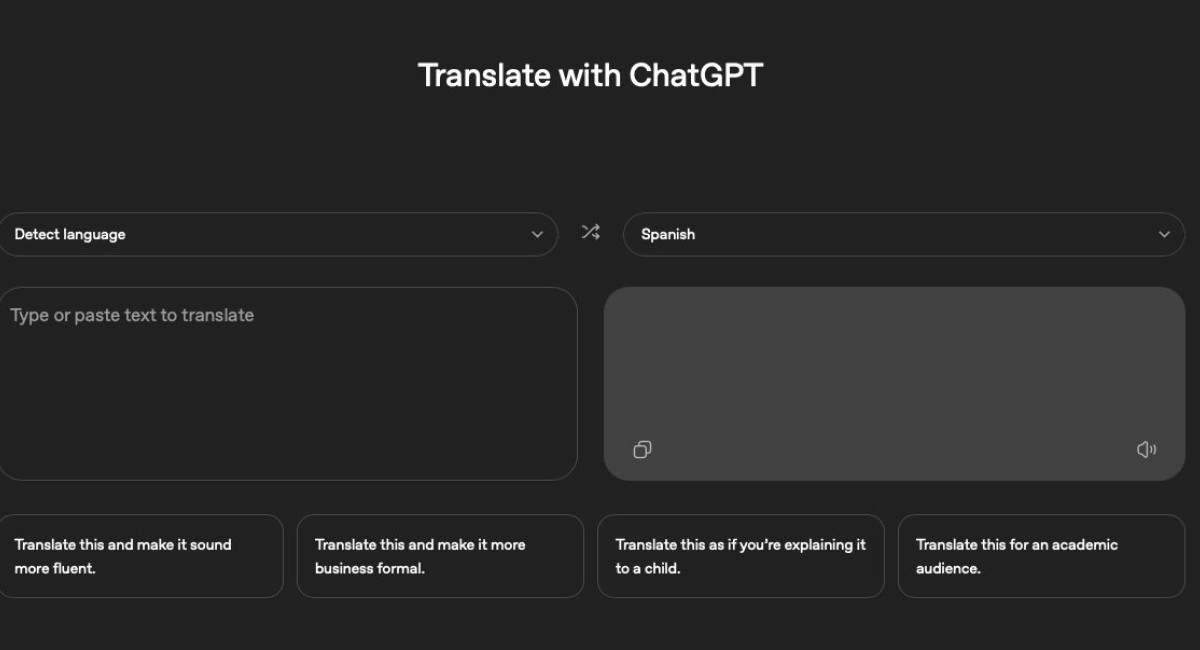
The discovery of this new tool, dubbed ChatGPT Translate, marks a significant shift in OpenAI’s product strategy. While users have long been able to ask the standard chatbot to translate text, this new initiative offers a specialized, standalone experience that mirrors the familiar dual-pane layout popularized by Google. This design choice is not accidental; it lowers the friction for users accustomed to existing tools while surreptitiously introducing them to a far more powerful underlying engine. The existence of this unannounced feature was brought to light through keen observation and testing, revealing a polished, user-friendly portal accessible via a specific web address, positioning it as a distinct utility rather than just another chat prompt.
What sets ChatGPT Translate apart from its traditional competitors is not merely its interface, but the versatility of its controls. In standard translation tools, the output is often static and binary; you input a sentence, and you receive a literal translation. OpenAI has introduced a layer of nuance that allows users to dictate the specific nature of the result. The tool includes options to adjust the tone of the translation instantly, offering presets such as "Call to Action," "Business Formal," "Academic," or "Explain it like a child." This functionality addresses one of the most persistent complaints about machine translation: the inability to adapt to the social or professional context of the conversation. A phrase meant for a boardroom should not sound the same as one spoken at a casual dinner, and this new tool places that control directly in the user's hands.
The technological capabilities extend far beyond simple text input. Embracing the multimodal nature of modern AI models, the interface supports a variety of input methods that make it a robust communication hub. Users can upload documents for full-file translation, use voice input to speak directly to the engine, or even upload images—such as a photo of a restaurant menu or a street sign—to receive instant interpretations. While Google has offered similar features through Lens and its mobile apps, the integration of these modalities into a unified, web-based AI environment suggests a more cohesive approach to breaking down language barriers. The ability to seamlessly switch between typing, speaking, and visual inputs caters to a mobile-first world where communication happens in flux.
Perhaps the most disruptive feature of ChatGPT Translate is its conversational memory. In traditional tools, if a translation misses the mark, the user is often stuck trying to manually rephrase the source text to trick the machine into a better result. With OpenAI’s approach, the translation is the beginning, not the end. Because the system is built on a conversational foundation, users can follow up with corrections or refinements. You can ask the tool to "make it sound more punchy" or "use a specific local dialect," and the AI adjusts the output in real-time. This interactive loop fundamentally changes the user relationship from passive recipient to active collaborator, ensuring higher accuracy and satisfaction.
The implications of this silent launch are profound for the tech industry. Google Translate has long benefited from its deep integration into the Chrome browser and the Android ecosystem, creating a moat that is difficult to cross. However, as users increasingly turn to large language models for information retrieval and content creation, the gravity is shifting. If OpenAI can offer a translation tool that is not only as accessible as Google’s but significantly more intelligent and adaptable, it could chip away at one of the search giant's most entrenched utilities. The move signals that OpenAI is transitioning from a provider of general-purpose models to a builder of specific, consumer-facing products that solve everyday problems.
MORE NEWS FOR YOU

 Help & Support
Help & Support 

